Animals That Live in the Mangrove Forest
Animals That Live in the Mangrove Forest
Mangroves Support:
- Microorganisms
- Algae
- Invertebrates
- Fish
- Reptiles and Amphibians
- Birds
- Mammals
Microorganisms

Mangroves are an important part of estuarine food webs, producing large amounts of leaf litter. Leaves drib from the mangrove trees and are speedily decomposed by fungi and bacteria. This decomposed thing is referred to as detritus which is flushed into the estuary by the outgoing tides. This provides a food source for marine life including economically important shrimp, venereal, and fish.
An estimated 75% of the game fish and 90% of the commercial species in south Florida are dependent upon the mangrove organization during at least part of their life cycles.
Algae
Algae play a vital role in mangrove customs food webs. Many organisms feed directly on micro and macroalgae that thrive within mangrove communities. The aerial root systems of mangrove copse provide a difficult substrate for the zipper of epiphytic algae such as diatoms and blue-green algae. Phytoplankton is an of import component of mangrove systems. Species richness is dependent upon the primary source of water and salinity levels equally well as seasonal and daily environmental fluctuations. The bulk of phytoplankton is washed into the mangroves from adjacent areas, including open ocean, freshwater, and estuarine environments.
-
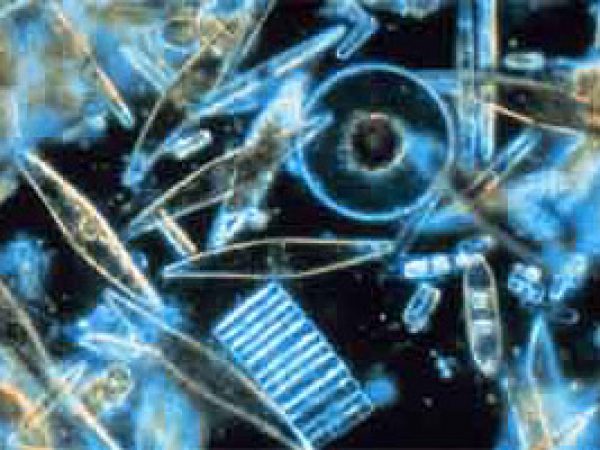

Marine diatoms. Photo © Prof. Gordon T. Taylor, Stony Brook University
-

Macroalgae. Photo © John Huisman
Invertebrates
Mangroves offer both hard and soft lesser habitats for a diverseness of invertebrate life. The all-encompassing root systems, muddy bottoms, and open up waters are all home to invertebrates that are well adapted to the temperature and salinity variations as well every bit tidal influences common to mangroves. These invertebrates feed on leaf litter, detritus, plankton, and other small animals. Snails, barnacles, bryozoans, tunicates, mollusks, sponges, polychaete worms, isopods, amphipods, shrimps, crabs, and jellyfish all live either on or in close proximity to mangrove root systems.
Some invertebrates thrive in the mangrove canopy, of which the most arable are the venereal. The mangrove tree crab, Aratus pisoni, resides in the canopy, feeding primarily on red mangrove leaves. Other venereal alive in the intertidal mud flats, utilizing leaf litter and detritus every bit a nutrient source.
Horseshoe crabs are scavengers and may be found amongst mangroves feeding on algae, invertebrates, and dead organisms. They are especially adapted to low oxygen waters, possessing up to 200 volume gills used for respiration.
-
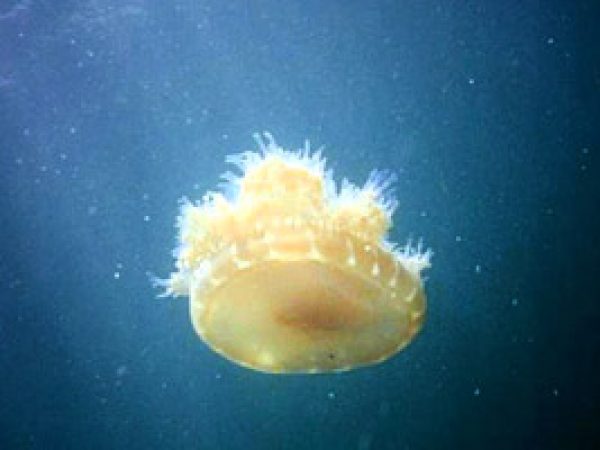

Upside-downwardly jellyfish. Photo © tools.coralreef.org
-
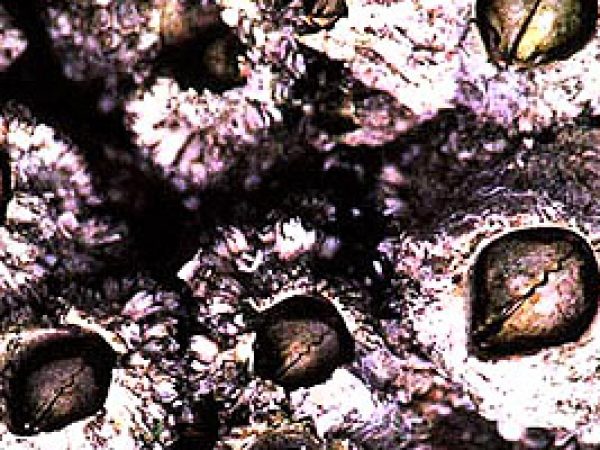
Barnacles. Photo courtesy National Park Service
-
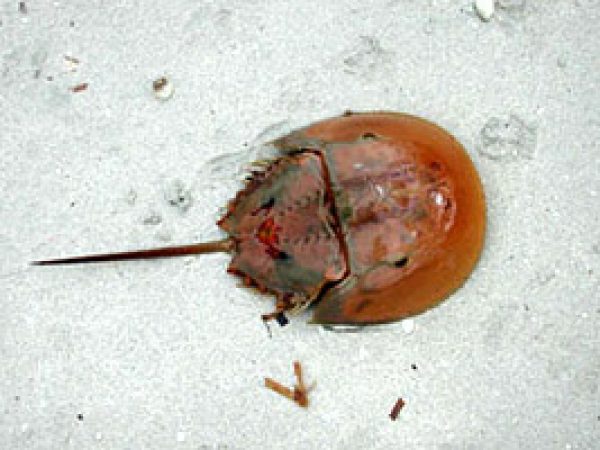

Horseshoe Crab. Photo © Cathleen Bester / Florida Museum
-
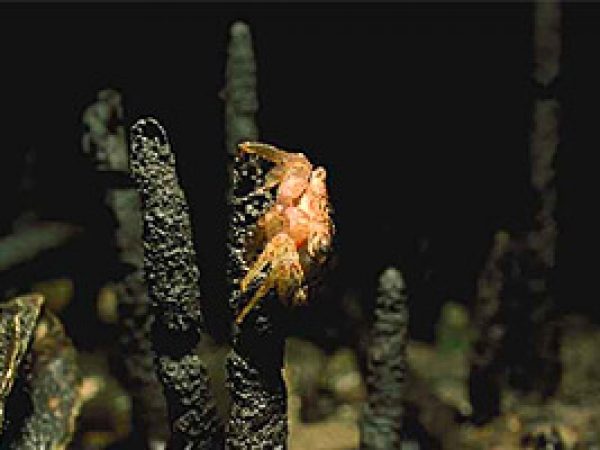

Mangrove tree crab. Photo courtesy South Florida H2o Direction District
-
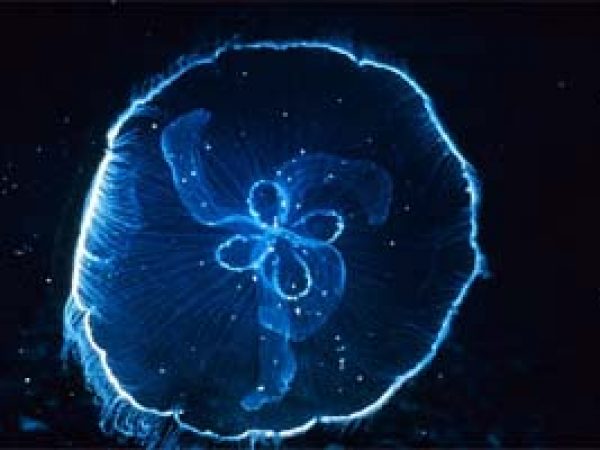
Moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita). Photo courtesy NOAA
-
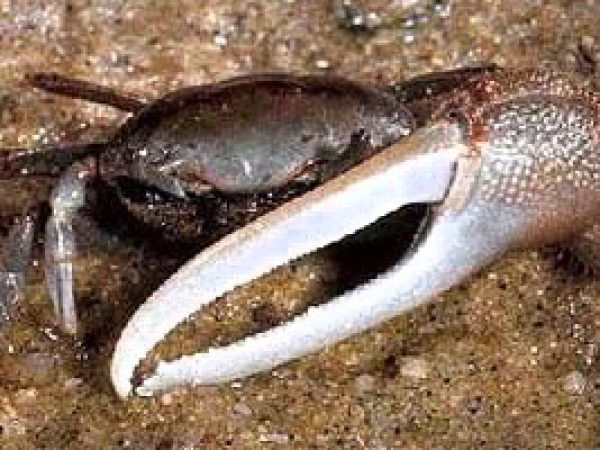

Fiddler crab (Uca pugnax). Photograph courtesy NOAA
Fish

The fishes found in south Florida mangroves represent marine species present in the Florida Bay along with the inclusion of freshwater species. During the rainy season, the increased menses of freshwater results in the appearance of freshwater species. However, the majority of dry out season species cannot survive in these low salinities and migrate to higher salinity areas offshore. Some marine species, such as snook (Centropomus undecimalis), prefer the lower salinity, remaining in the mangroves during the entire twelvemonth.

Mangrove roots provide an ecologically important habitat for a wide diverseness of fish. Jacks (Caranx spp.), sheepshead (Archosargus probatocephalus), grunts (Haemulon spp.), gobies (Gobiosoma spp.), schoolmasters (Lutjanus apodus), greyness snappers (Lutjanus griseus), and small goliath grouper (Epinephelus itajara) as well as many other species of fish can be institute among the tangled roots of red mangroves. Tarpon (Megalops atlanticus) cruise in waters adjacent to mangrove roots. The spotted seatrout (Cynoscion nebulosus) also thrive in mangroves and can tolerate high turbidity, taking advantage of the prey fish in the mangroves and seagrass beds. The florida gar (Lepisosteus platyrhincus) is a top-level carnivore, feeding on a multifariousness of smaller fishes.

Mangroves are important plant nursery areas for the sport and commercial line-fishing industry. Greyness snapper (Lutjanus griseus), spotted seatrout (Cynoscion nebulosus), and red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) are amongst the species that utilize the mangrove primarily as plant nursery areas. The mangrove roots and shallow waters offer shelter from predators until the juveniles reach a size big enough to avert most predators. These three species mentioned above are highly prized by sport fishers. Equally mangrove habitats are destroyed, the sport and commercial fisheries decline equally a direct consequence.
Reptiles and Amphibians
-
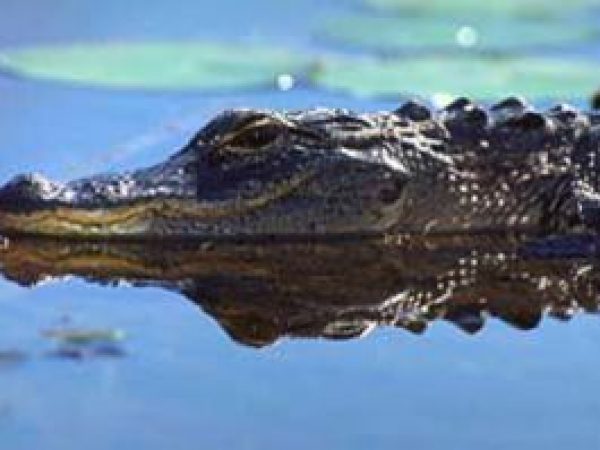

American alligator. Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District
-
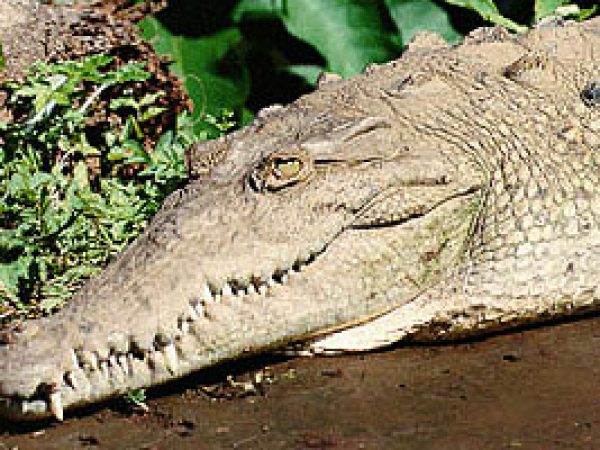

American Crocodile (Crocodylus acutus). Photograph courtesy U.Due south. Fish and Wildlife Service
American alligators (Alligator mississippiensis) and American crocodiles (Crocodylus acutus) are both residents of mangrove habitats. The American alligator ranges throughout the southeastern U.Due south., and is found only in low salinity areas of Florida mangroves. On the other hand, the American crocodile is quite rare, relying heavily on mangrove habitats for their survival. In recent years, the range of this reptile has decreased considerably due to devastation of habitat and increase in human activity within the Florida Keys. The American crocodile at present occurs in the due north Florida Bay and nearby swamps, besides as the north end of Key Largo.
Nine species of snakes reside in the mangroves of Florida.
Species residing in mangroves include:
-

Mangrove water serpent. Photo © Kenneth Krysko
-

Eastern indigo snake (Drymarchon coaris couperi). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wild animals Service
-
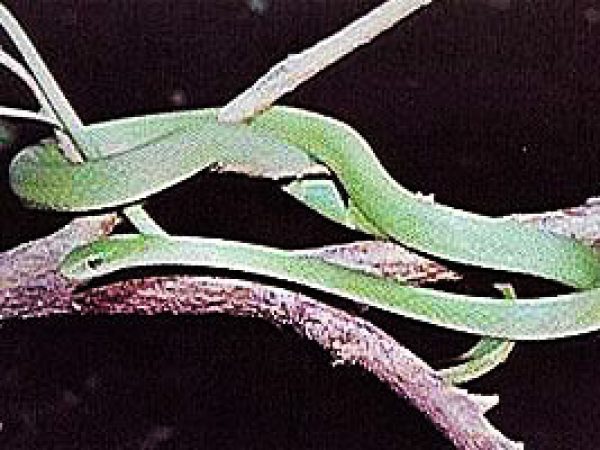
Crude Dark-green ophidian (Opheodrys aestivus carinatus). Photograph courtesy U.South. Fish and Wild animals Service
-
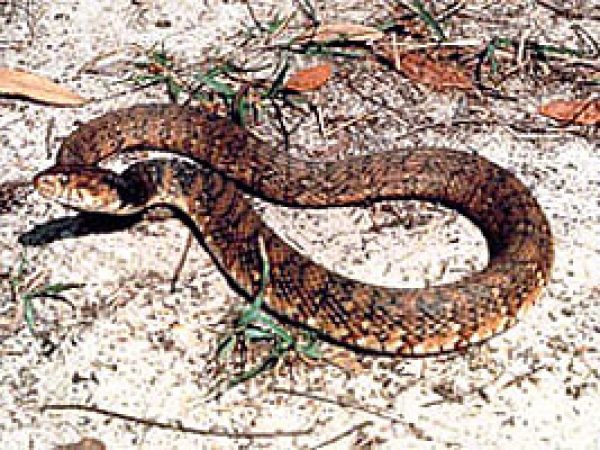

Florida banded water ophidian (Nerodia fasciata pictiventris). Photo courtesy U.S. Department of Tranportation
-
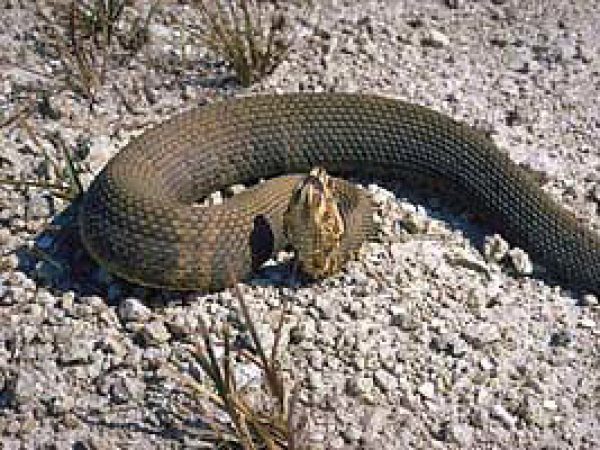

Eastern cottonmouth. Photo courtesy South Florida H2o Direction District
- mangrove water snake (Nerodia clarkii compressicauda)
- Florida green water ophidian (Nerodia floridana)
- rosy rat ophidian (Elaphe guttata rosacea)
- Florida king serpent (Lampropeltis getula floridana)
- Atlantic saltmarsh snake (Nerodia clarkii taeniata)
Anoles, including the green anole (Anolis carolinenesis), brown anole (Anolis sagrei), and the bark anole (Anolis distichus), reside in the trees within mangroves, feeding on insects.
-
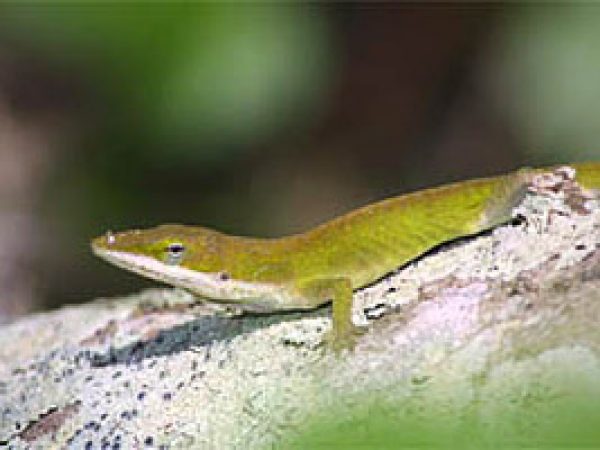

Green Anole (Anolis carolinensis). Photo © Adam P. Summers, Museum of Vertebrate Zoology
-
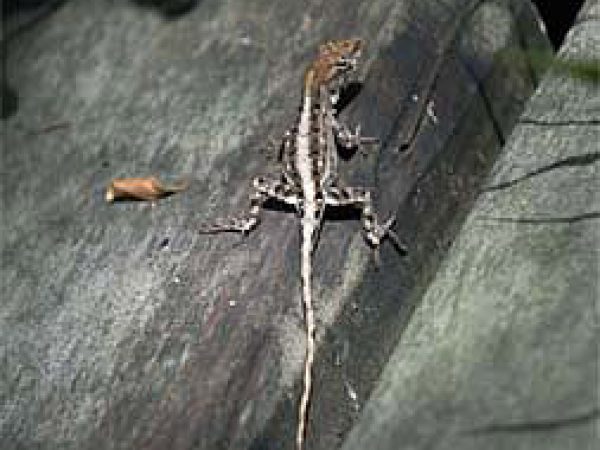

Brown Anole (Anolis sagrei). Photo courtesy U.Due south. Geological Survey
Freshwater species of turtles are constitute nearly the headwaters of mangrove river systems. The ornate diamondback terrapin (Malaclemys terrapin macrospilota and M. t. rhizophorarum) relies upon mangroves as its primary habitat along with iii other species of freshwater turtles occur in mangroves. Also associated with mangrove vegetation during at least some betoken in their life histories are sea turtles. The loggerhead (Caretta caretta) and dark-green body of water turtle (Chelonia mydas) apply the mangroves as juvenile nurseries, receiving protection from predators as well equally an surface area rich in food. The green sea turtle and Hawksbill body of water turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) take been observed feeding on mangrove roots and associated submerged vegetation. The Atlantic ridley sea turtle (Lepidochelys kempii) is unremarkably observed in the mangrove-lined bays of south Florida.
-
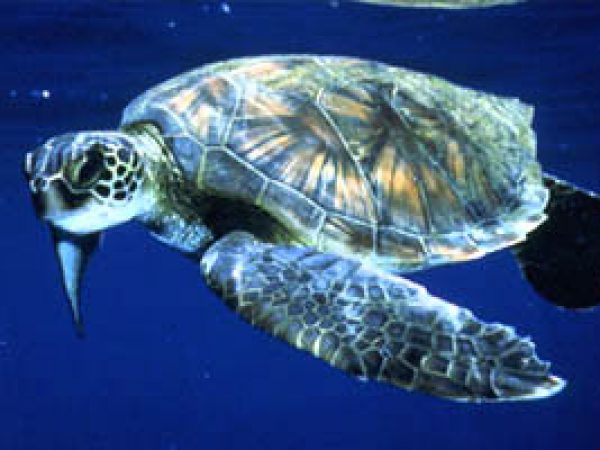

Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wild fauna Service
-
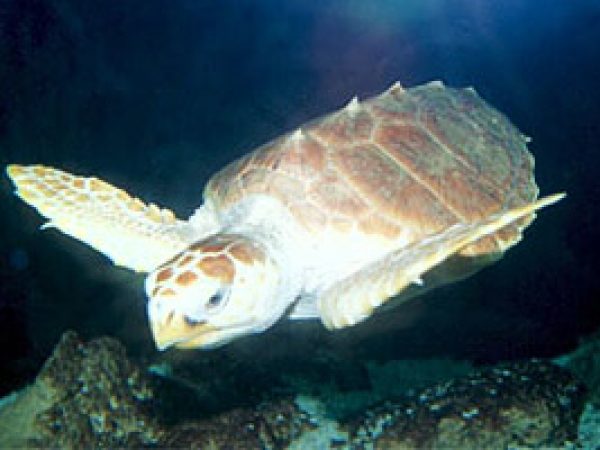

Loggerhead Body of water Turtle © John White
-
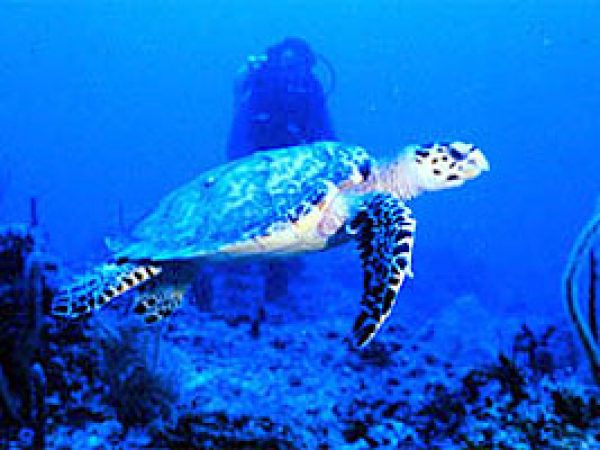

Hawksbill Ocean Turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata). Photo courtesy NOAA
Only three species of amphibians are known to occur in mangroves. This is due to the disability of osmoregulatation in saltwater equally well as lack of detailed surveys in low salinity regions within mangrove systems. The occurrence of more amphibian species within this habitat is highly suspected, although unknown at this time.
Species known to occur in mangroves include:
-

Giant toad. Photo © Hugo Claessen
-

Squirrel Treefrog (Hyla squirella). Photograph courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
-

The Cuban treefrog is an introduced species in south Florida courtesy South Florida H2o Management District
Birds
The mangroves of due south Florida provide a habitat for many bird species. The shallow waters and exposed mudflats of the mangroves brand this habitat ideal for probing shoreline birds such as plovers and sandpipers. Long-legged wading birds utilize these and deeper waters along mangrove-lined waterways. Herons, egrets, bitterns, spoonbills, limpkins, and ibis are among the wading birds that visit mangroves in search of food.
-

Great egret (Casmerodius albus). Photo courtesy Southward Florida Water Management District
-
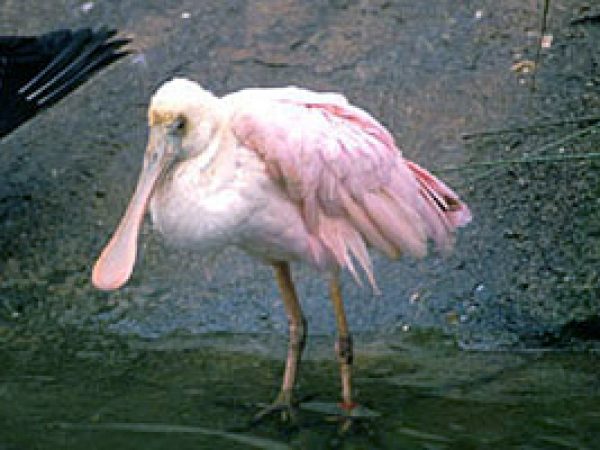

Roseate spoonbill. Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wild fauna Service
-
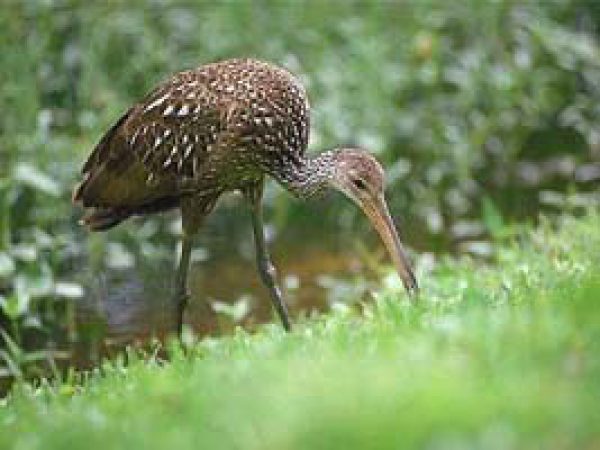

Limpkin (Aramus guarauna). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District
-
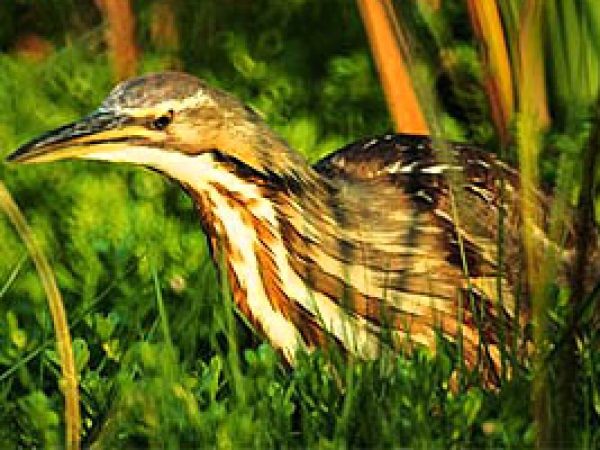

American bittern (Botaurus lentiginosus). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management Commune
-
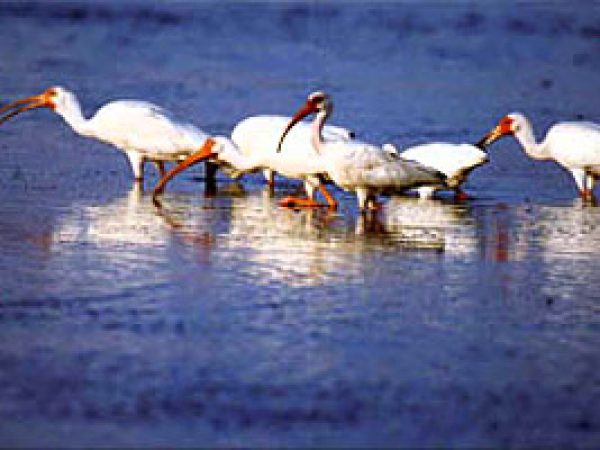

White ibis (Eudocimus albus). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
-
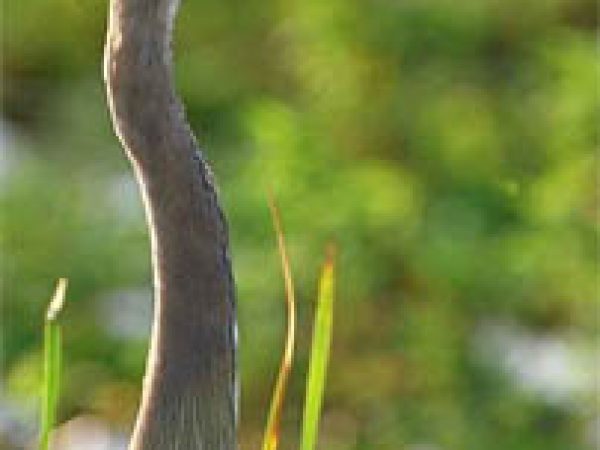

Great Blue Heron (Ardea herodias). Photo courtesy Due south Florida Water Management District
-
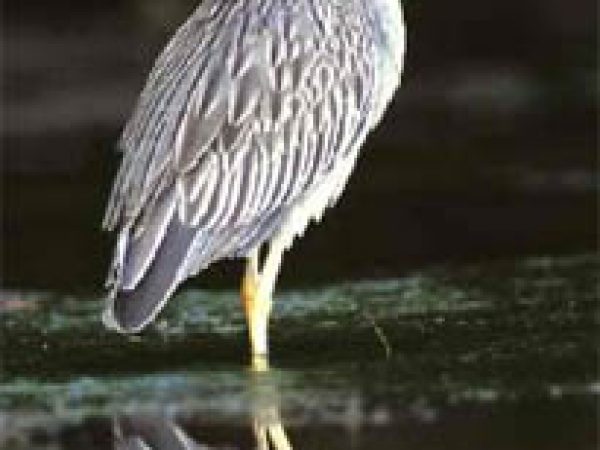

Xanthous-crowned Dark Heron (Nyctasnassa violacea). Photograph courtesy Due south Florida Water Management District
-
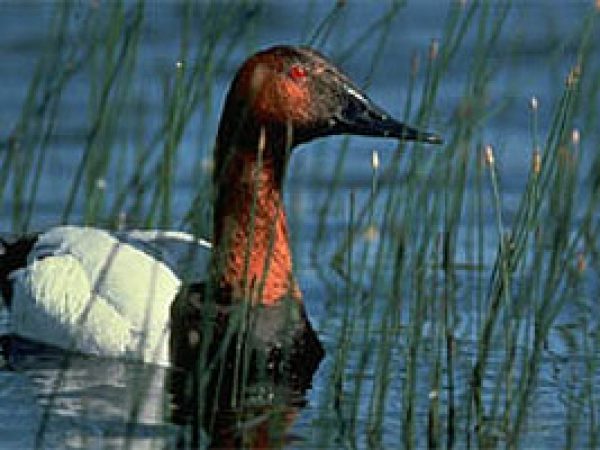

Canvasback (Aythya valisineria). Photograph courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
White Ibis (Eudocimus albus) feed on crabs while the roseate spoonbill (Ajaia ajaja) preys on mollusks and other invertebrates living inside the sediments. Yellow-crowned night herons (Nyctasnassa violacea) and American bitterns (Botaurus lentiginosus) feed on a multifariousness of prey, including crabs, crayfish, frogs and mice likewise as modest fishes. Mangroves also provide breeding habitat for wading birds. The entire Everglades population of the woods stork nests only in mangroves.
20-9 species of ducks, grebes, loons, cormorants, and gallinules have been observed in the mangrove habitats of south Florida. These floating/diving birds feed on fishes, plant materials, and invertebrates. Some of these waterfowl are year round residents, while others occur during migration or as winter visitors.
Species include:
-
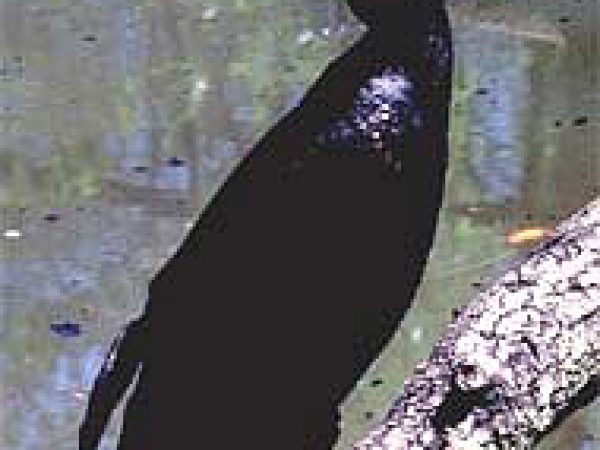

Double-crested cormorant (Phalacrocorax auritus). Photo courtesy U.South. Geological Survey
-
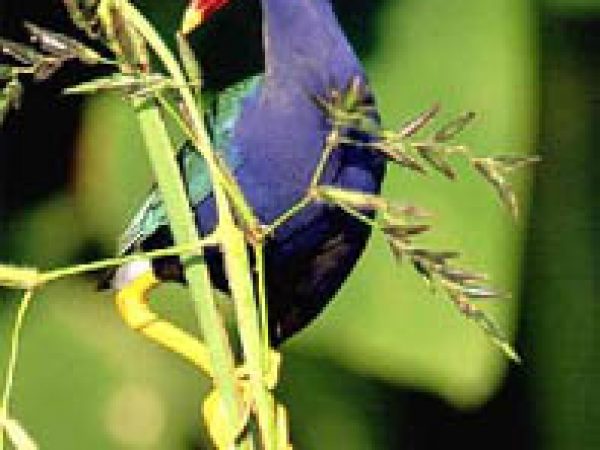

Purple gallinule (Porphyrula martinica). Photo courtesy Due south Florida Water Management District
-
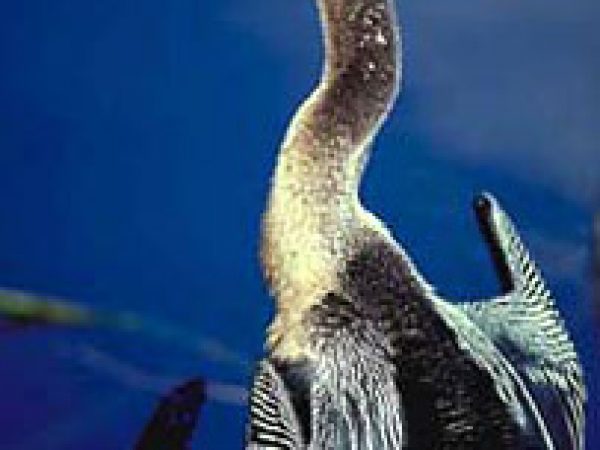

Anhinga (Anhinga anhinga). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
-
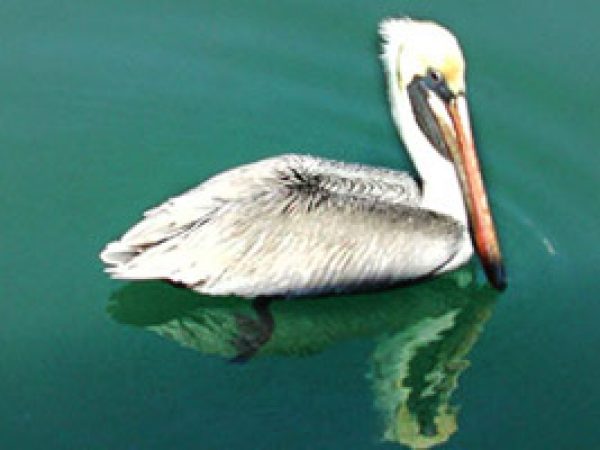

Brown pelican (Pelecanus occidentalis). Photo Cathleen Bester / Florida Museum
-
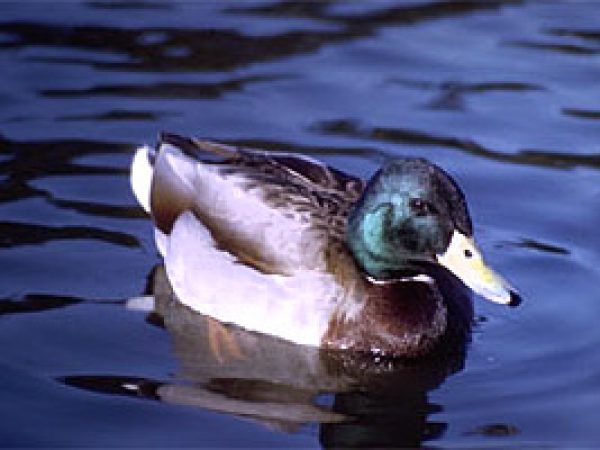

Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos). Photo © Dr. Antonio J. Ferreira, California University of Sciences
-

Pintail (Anas acuta). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
-

Lesser scaup (Aythya affinis). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
Birds of prey include permanent residents, summertime residents, and winter visitors of mangrove habitats. The southern bald eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus leucocephalus), osprey (Pandion haliaetus), and peregrine falcon (Falco columbarius) depend upon mangroves for their survival in south Florida. The bald hawkeye and osprey feed extensively on the fishes that occur in mangroves. These species also roost and nest inside the mangrove tree awning.
-

Southern bald hawkeye (Haliaeetus leucocephalus leucocephalus). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District
-

Osprey (Pandion haliaetus). Photo courtesy NOAA
-
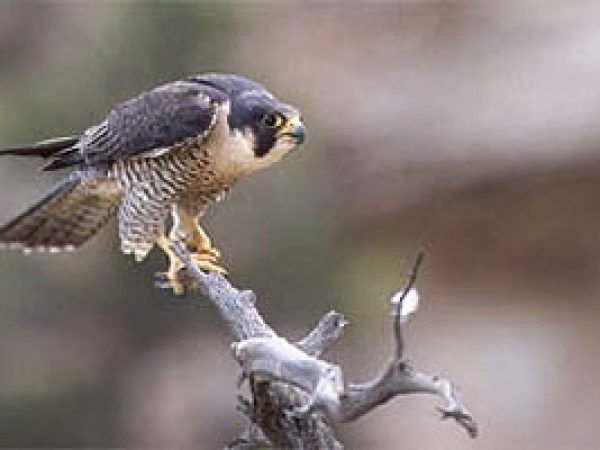

Peregrine falcon (Falco columbarius). Photo courtesy Southward Florida Water Management Commune
-
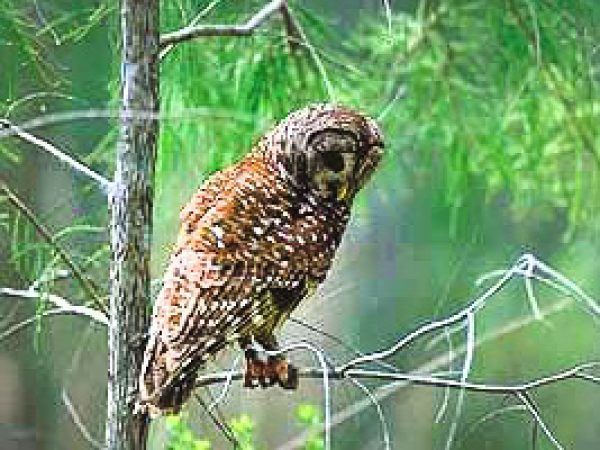

Barred owl (Strix varia). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District
-
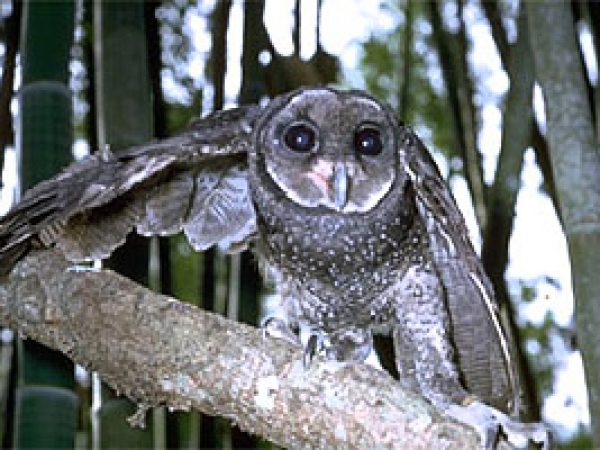

Befouled owl (Tyto alba). Photo © R. Straatman, California Academy of Sciences
-
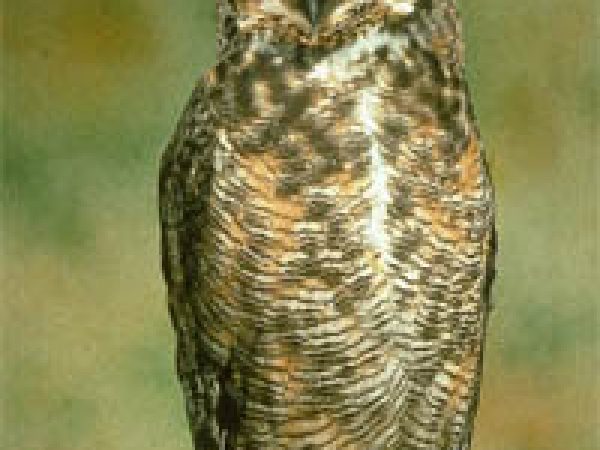

Bully horned owl (Bubo virginianus). Photo courtesy National Park Service
-
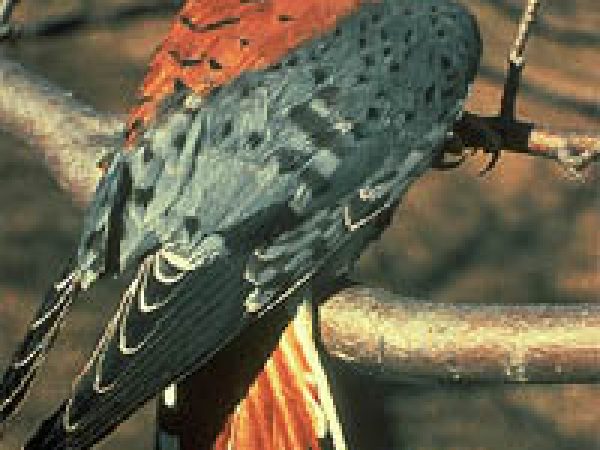

American kestrel (Falco sparverius). Photograph courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
-
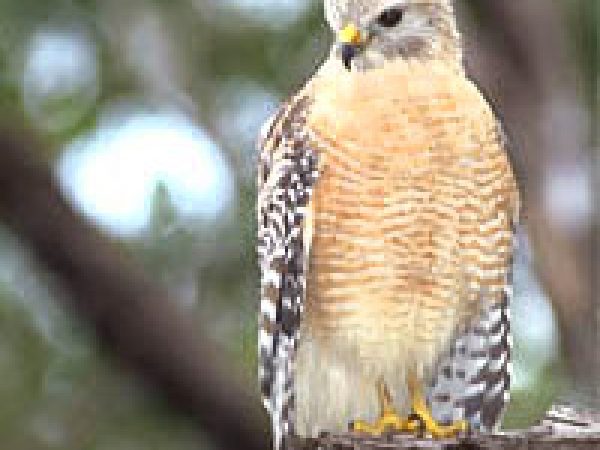

Carmine-shouldered hawk (Buteo lineatus). Photo © Gerald and Vitrify Corsi, California Academy of Sciences
-
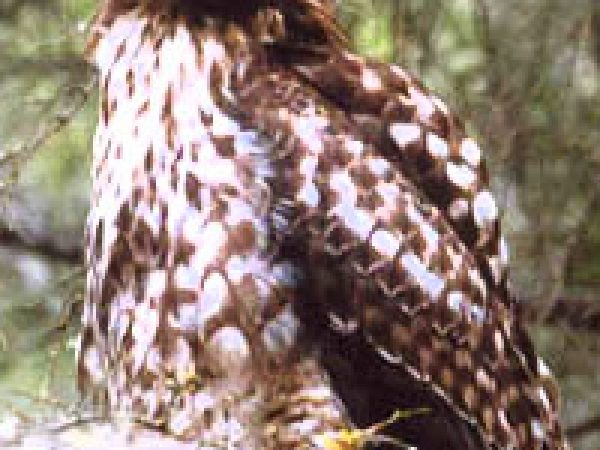

Ruby-red-tailed hawk (Buteo jamaicensis). Photograph courtesy Bureau of Land Management
-
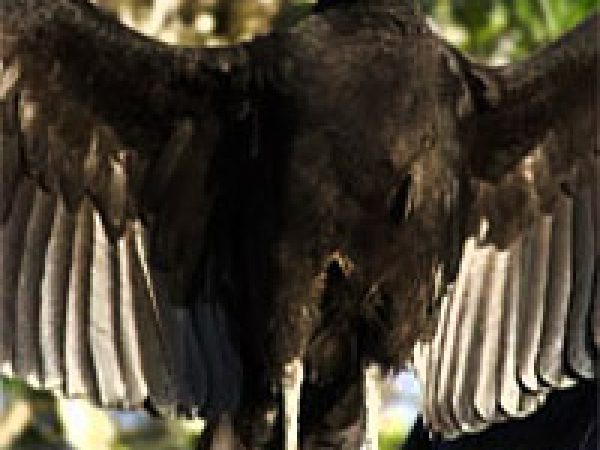

Blackness vulture (Coragyps atratus). Photo courtesy S Florida H2o Direction District
-

Turkey vulture (Cathartes aureola). Photo courtesy Southward Florida H2o Management District
Other birds of prey that frequent mangrove systems include:
- Cooper's hawk (Accipter cooperii)
- marsh hawk (Circus cyaneus)
Mammals
Carnivores residing in the mangroves of southward Florida include:
-

Florida panther (Felis concolor). Photo courtesy S Florida Water Direction District
-

Striped skunk (Mephitis mephitis). Photograph courtesy National Park Service
-

Raccoon (Procyon lotor). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
-
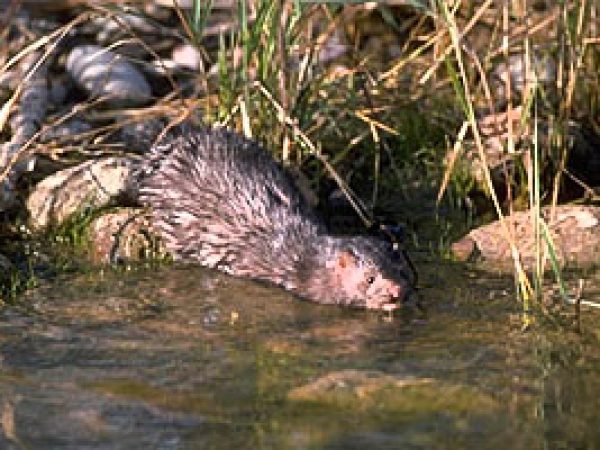

Mink (Mustela vision). Photo © Gerald and Buff Corsi, California Academy of Sciences
-
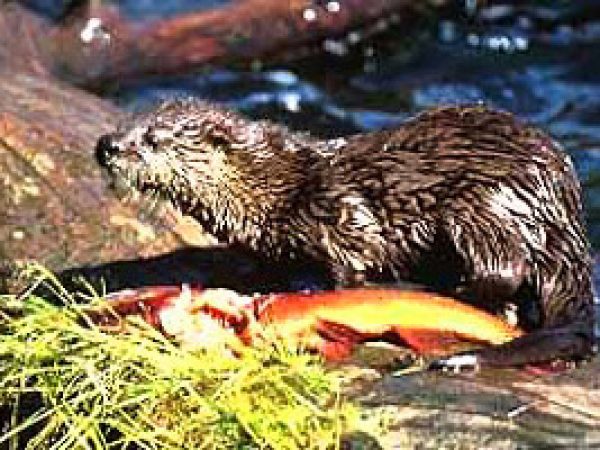

River otter (Lutra canadensis). Photograph courtesy National Park Service
-
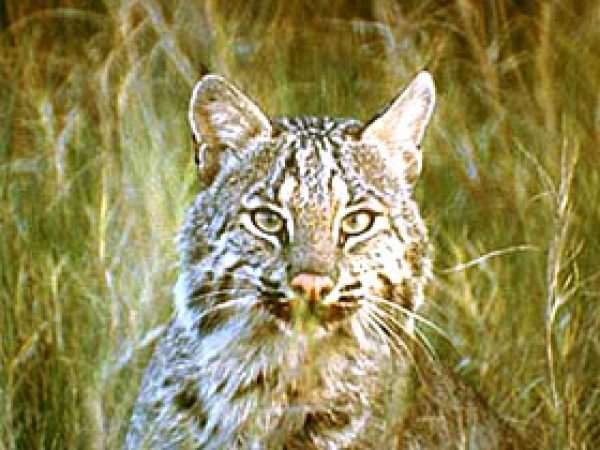

Bobcat (Lynx rufus). Photo courtesy U.South. Fish and Wildlife Service
- gray fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus), not shown
- black bear (Ursus americanus), not shown
The Florida panther is rarely observed, nevertheless virtually of the contempo sightings have been inside the everglades mangrove systems. Simply l-60 panthers remain in Florida – the greatest threat to this critically endangered true cat is habitat destruction. Coastal hammocks and mangroves are vital for the continued survival of this panther.
Other mammals residing in these areas include:
-
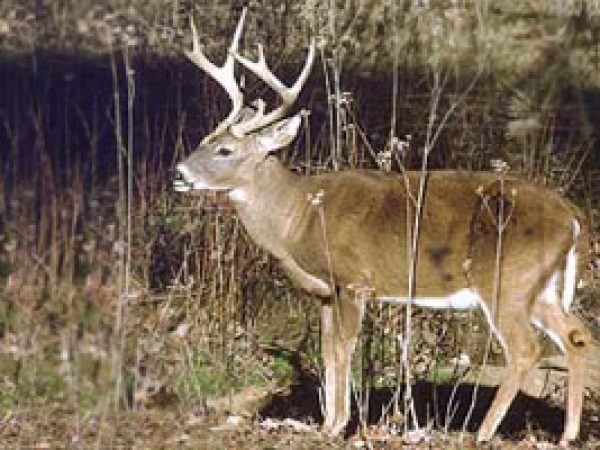

White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Photo courtesy U.Due south. Geological Survey
-

Opossum (Didelphis virginiana). Photo courtesy National Park Service
-

Marsh rabbit (Sylvilagus palustris). Photo courtesy National Park Service
- central deer (Odocoileus virginianus clavium), not shown
- cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus), non shown
- marsh rice rat (Oryzomys palustris), not shown
- argent rice rat (O. argentatus), non shown
Marine mammals found along mangrove-lined waterways include bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) and manatees (Trichechus manatus). Dolphins feed on fishes associated with mangrove systems. Equally an herbivore, the manatee feeds on seagrasses and other submerged aquatic plants found outside mangroves. However, manatees are frequently observed swimming in canals, littoral rivers, and other waters shut in proximity to mangroves.
-

Bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). Photo courtesy NOAA
-

Manatee (Trichechus manatus). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
Glossary terms on page:
- detritus: Expressionless or decaying organic matter.
- estuary: area where freshwater meets the ocean, creating a salinity gradient from pure freshwater (0 ppt) to full-strength seawater (35 ppt).
- substrate: the material upon or within an organism lives or grows, including soil, plants, animals and rocks.
- epiphytic: any organisms that abound on the blades of seagrasses, including algae, diatoms, and other encrusting organisms.
- phytoplankton: microscopic plants that depend upon water currents for transportation, principal producers in aquatic environments.
- plankton: organisms dependent on h2o move and currents every bit their means of transportation, including phytoplankton, zooplankton, and ichthyoplankton.
- salinity: concentration of total salts dissolved in water, usually measured in parts per thousand.
- diversity: refers to the variety of species inside a given association, areas of loftier diverseness are characterized by a great diverseness of species.
- polychaete: grade of annelid worms that includes bristle and feather squeegee worms.
- canopy: uppermost layer of branches in a forest.
- intertidal: the surface area likewise known every bit the littoral zone which is covered past water during high tide and exposed at low tide.
- turbidity: measurement of water clarity, turbidity increases when more than light is scattered by particles suspended in the water.
- population: a group of interacting individuals of the same species, surface area, or community.
- herbivore: an creature that feeds on plants.
Animals That Live in the Mangrove Forest
Source: https://www.floridamuseum.ufl.edu/southflorida/habitats/mangroves/mangrove-life/#:~:text=Snails%2C%20barnacles%2C%20bryozoans%2C%20tunicates,most%20abundant%20are%20the%20crabs.

Komentar
Posting Komentar